- Ứng dụng
- SẢN PHẨM
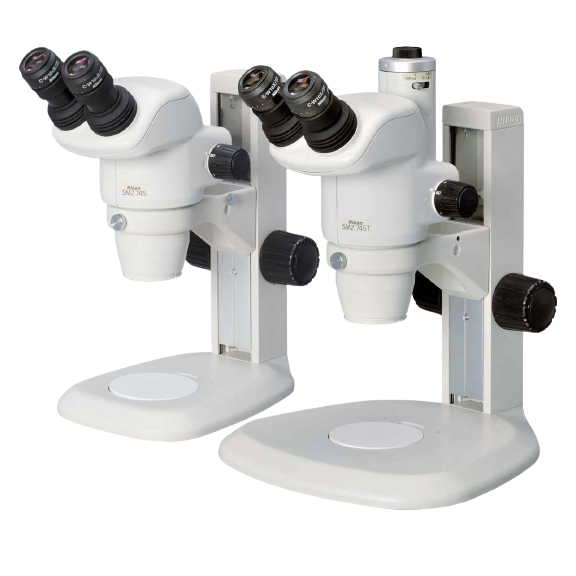
- Kính hiển vi công nghiệp
- Camera & Phần mềm đo lường
- Thiết bị đo lường NIKON
- Máy đo quang học (2D/3D) Trung Quốc
- Máy đo chạm 3D
- Máy Đo bề mặt và biên dạng
- Thiết bị đo công nghiệp
- Thiết bị đo hiện trường
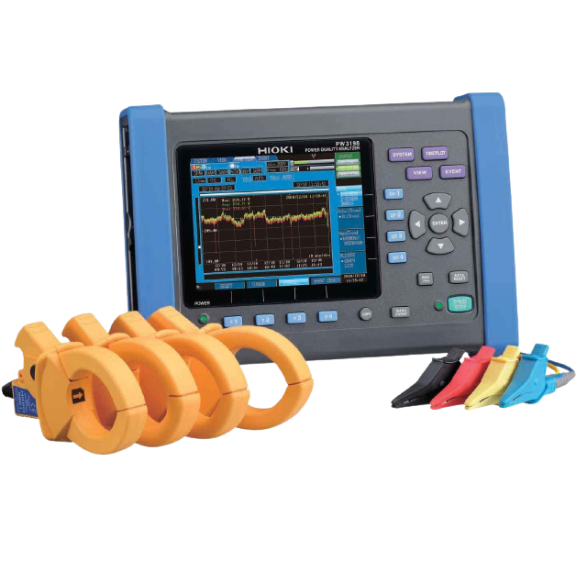
- Thiết bị đo kiểm điện áp, cường độ, công suất
- THIẾT BỊ GHI DỮ LIỆU ĐA KÊNH
- THIẾT BỊ ĐO LCR, THIẾT BỊ PHÂN TÍCH TRỞ KHÁNG, ĐO ĐIỆN DUNG
- THIẾT BỊ GHI DỮ LIỆU NHỎ GỌN, THIẾT BỊ GHI DỮ LIỆU NHIỆT ĐỘ
- THIẾT BỊ ĐO ĐIỆN TRỞ, THIẾT BỊ KIỂM TRA PIN
- THIẾT BỊ ĐO SIÊU ĐIỆN TRỞ
- THIẾT BỊ KIỂM TRA AN TOÀN ĐIỆN, THIẾT BỊ ĐO ĐIỆN TRỞ CÁCH ĐIỆN/DÒNG RÒ/HIPOT
- THIẾT BỊ PHÂN TÍCH CHẤT LƯỢNG ĐIỆN, THIẾT BỊ GHI CÔNG SUẤT
- ĐẦU ĐO / CẢM BIẾN DÒNG ĐIỆN, ĐẦU ĐO ĐIỆN ÁP, CẢM BIẾN CAN
- TỪ TRƯỜNG, NHIỆT ĐỘ, MỨC ÂM THANH, LUX, XOAY
- Thiết bị đo áp suất và cảm biến áp suất
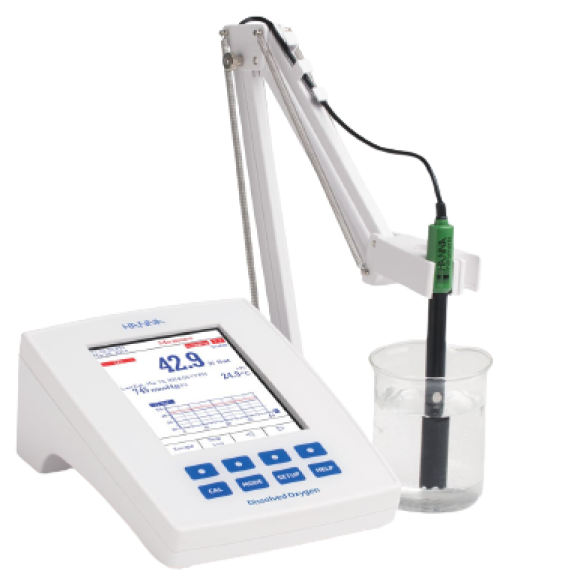
- Máy đo kiểm trong phòng thí nghiệm
- THƯƠNG HIỆU
- Về chúng tôi
- Tin tức